

Moreover, fault tolerance is an issue to consider. Link aggregation is needed in core switches, ensuring distribution switches delivering network traffic to the core layer as efficiently as possible. Core switches should perform advanced DDoS protection using layer 3 protocols to increase security and reliability. Connectivity between a distribution and core switches is accomplished using layer 3 links. Typically core switches are layer 3 switches, performing both switching and routing functions. FS provides switches with hot-swappable fans and power supply modules for better redundancy. With redundant power supplies, when one supply fails, the other one will instantly start running, ensuring the whole network unaffected by the maintenance. Imagine that the switches lose power when the networking is running, the whole network would shut down when you are going to perform a hardware replacement. The redundant power supply is another feature that should be considered. As often the case, core layer switches are generally equipped with redundant cooling systems to help the switches cooling down while they are running. Since the core layer switches carry much higher workloads than the access switches and distribution switches, they are generally hotter than the switches in the other two layers, the cooling system should be taken into consideration. For instance, network designers can determine the necessary forwarding rate of core switches by checking and examining the various traffic flow from the access and distribution layers, then identify one or more appropriate core switches for the network.Ĭore switches pay more attention to redundancy compared with other switches.
The concrete forwarding rate largely depends on the number of devices in the network, the core switches can be selected from the bottom to the top based on the distribution layer devices. Compared with the access layer switches and distribution switches, core switches must provide the highest forwarding rate and switching capacity as much as possible. The packet forwarding rate and switching capacity matter a lot to the core switch in enterprise networking. Except for considering the basic specifications like port speed and port types, the following factors should be considered when choosing core switches for an enterprise network design. Simply put, core layer switches are generally layer 3 switches with high performance, availability, reliability, and scalability.
BACKBONE MEANING IN NETWORKING HOW TO
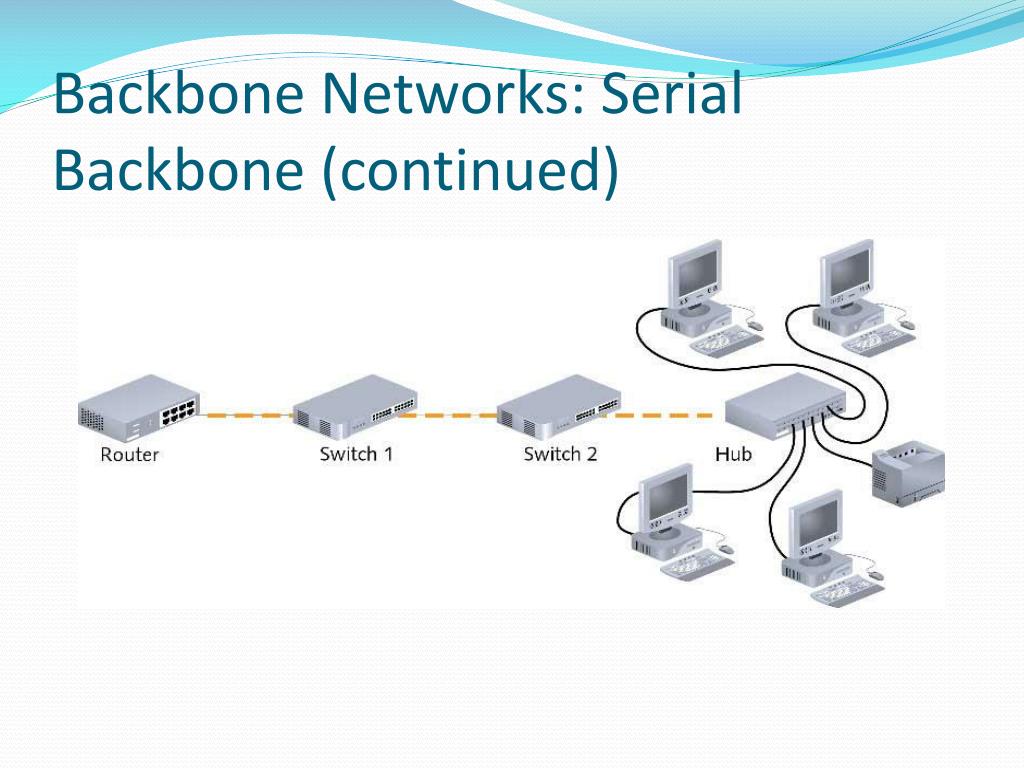
More information about the collapsed core is available in How to Choose the Right Distribution Switch?įactors to Consider When Choosing Core Switches for Enterprises Note: In small networks, it is often the case to implement a collapsed core layer, combining the core layer and the distribution layer into one as well as the switches. To ensure the high-speed traffic transfer, core switches should not perform any packet manipulation such as Inter-Vlan routing, Access Lists, etc., which are performed by the distribution devices. For most of the cases, core switches manage the high-speed connections, such as 10G Ethernet, 40G Ethernet or 100G Ethernet. They are usually the most powerful, in terms of forwarding large amounts of data quickly. In these three layers, core switches require most highly in the switch performance. Located at the core layer of enterprise networking, a core layer switch functions as a backbone switch for LAN access and centralizes multiple aggregation devices to the core. The core layer always consists of high-speed switches and routers optimized for performance and availability.įigure 1: Core Switches in the three-tier architecture So it is important for core switches to send large amounts of packets as much as possible. It aggregates all the traffic flows from distribution layer devices and access layer devices, and sometimes core switches need to deal with external traffic from other egresses devices. In the enterprise hierarchical network design, the core layer switch is the topside one, which is relied on by the other access and distribution layers. Read to find more details about the factors to consider when choosing the core switches. So how to select the most suitable core switches for the campus network and enterprise networks is important in the long term. Traffic growth at the access layer and distribution layer will impact the performance of core switches. Core switches lie at the heart of the enterprise networks and take the duty for high-speed routing and switching.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
